Collagen vascular Autoimmune Diseases
Connective Tissue Disorders
Antinuclear Antibodies (ANA)
Serological tests for antinuclear antibodies play an important role in the diagnosis of various connective tissue autoimmune diseases:
- Systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE)
- Systemic sclerosis (SSc)
- Mixed Connective Tissue Disorders
- Sjogren's syndrome
Antinuclear antibodies (ANA) are detected by various methods including indirect immunofluorescence (IFA) on HEp-2 or other substrates and by ELISA.
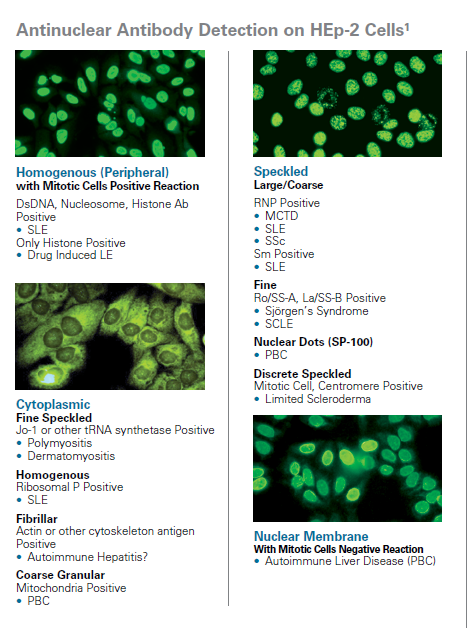
ANAs have different patterns of fluorescence associated with a specific disease or subgroup of collagen vascular disorders:
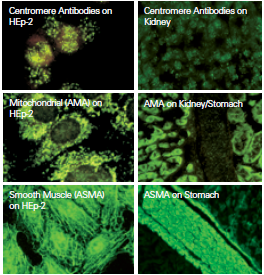
|
Systemic Sclerosis |
Nuclear Antibodies |
|
CREST Variant SSc |
Centromere Antibodies |
|
Systemic Lupus Erythematosus (SLE) |
homogeneous / Rim antibodies |
Accurate identification of molecular specificities is essential as they may be associated with a particular disease or disease subset.
Extractable Nuclear Antigen (ENA) Antibody
Autoantibodies directed against extractable nuclear antigen (ENA) antibodies are useful in the diagnosis and monitoring of various systemic connective tissue disorders.
|
SLE (30-40%) |
Sm Antibodies |
|
SLE (35-45%) |
RNP Antibodies |
|
Subacute Cutaneous Lupus Erythematosus (LE) (60%) |
Ro / SS-A Antibodies |
DNA Antibodies (Crithidia lucilliae)
Antinuclear antibodies (ANA) include antibodies against nuclear antigens such as DNA, histone and various extractable nuclear antigens (ENA).
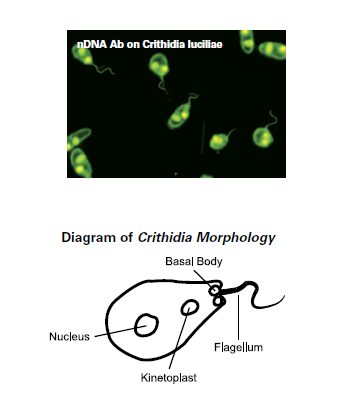
The microorganism Crithidia lucilliae is a flagellate and contains a special organelle called kinetoplast. This kinetoplast is a modified mitochondrion with double-stranded DNA (nDNA) without histones and no other core antigens that could cross-react with autoantibodies other than dsDNA antibodies.
The kinetoplast is smaller and rounder than the cell nucleus and lies between it and the basal body.
Antibodies to nDNA are specific for systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE).
Within nDNA antibodies, three specificities occur:
- dsDNA antibodies that only react with dsDNA (double-stranded DNA)
- ssDNA antibodies that only react with ssDNA (single-stranded DNA)
- ds / ssDNA antibodies that react with both dsDNA and ssDNA
Histone Antibodies
Antibody to histone, a protein associated with DNA in the nucleus of eukaryotic cells, occurs in a number of clinical conditions:
- Systemic Lupus Erythematosus (SLE)
- Drug-Induced Lupus Erythematosus (LE)
- Drug-Induced ANA-Positive Patients
IgG and IgM histone antibodies are found in approximately 50% of asymptomatic SLE patients and in 83% of active SLE patients.
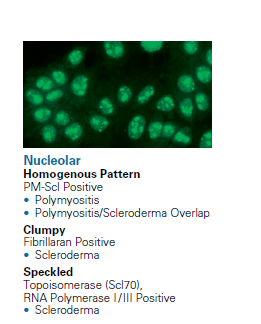
Polymyositis Scleroderma (PM-Scl) Antibodies
Antibodies to polymyositis scleroderma (PM-Scl), also known as the human exosome complex, are found in patients with polymyositis scleroderma (PM-SSc) overlap syndrome and related disorders.
Determination of Antibodies in Diseases of Connective Tissue:
- ANA
- Ro / SS-A, La / SS-B, Sm, RNP, Sc-70, Jo-1, centromeres, histones, and dsDNA
- Div. Substrate / Tissue Sections (liver, stomach, kidney of mouse, rat, ...)
- HEp2 Cells
- ENP Antibodies
- Sm Antibodies
ImmcoStrip™ ANA Line Immunoassay (LIA)
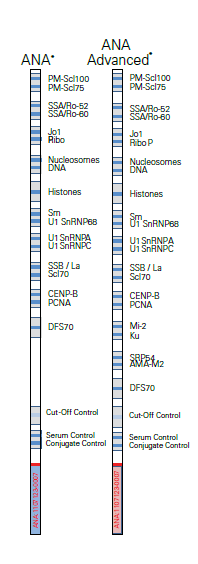
- nDNA Antibodies (Crithidia luciliae)
- dsDNA Antibody ELISA IgG
- Histone Antibody ELISA
- PM-Scl Antibody ELISA
Rheumatoid Arthritis
Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is one of the most common autoimmune diseases and affects 1-2% of the population.
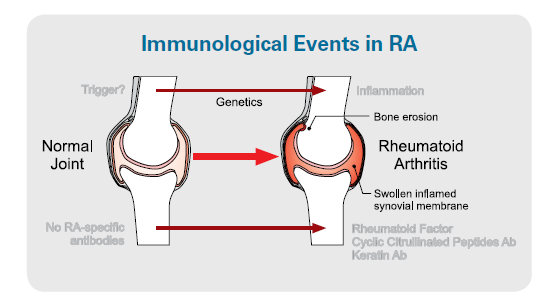
Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is a connective tissue disease characterized by chronic inflammation of the synovial joints with cartilage and bone destruction.
The diagnostic criteria are the rheumatoid factor (RF) and antibodies against cyclic citrullinated peptides (CCP).
Rheumatoid Factor (RF)
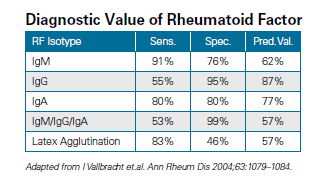
Rheumatoid factor (RF) is present in 70-90% of patients with rheumatoid arthritis (RA) and included in the ACR classification criteria.
According to the revised ACR criteria, the patient suffers from rheumatoid arthritis (RA) when three or more joints are affected and the rheumatoid factor (RF) is positive.
The rheumatoid factor (RF) has a sensitivity of 93.5% and a specificity of 89.3% for rheumatoid arthritis.
Elevated IgM and IgA RF isotypes are highly specific for rheumatoid arthritis.
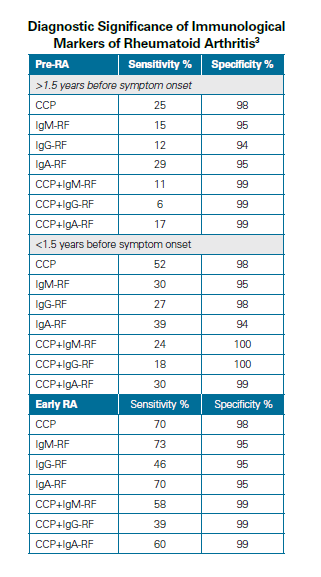
Antibodies to Citrullinated Peptides (CCP)
Recent studies have shown that antibodies to citrullinated antigens in the serums of rheumatoid arthritis patients are useful in determining the diagnosis and prognosis of rheumatoid arthritis (RA).
CCP antibodies can be detected years before the appearance of clinical symptoms.
Determination of antibodies in rheumatoid arthritis:
- RF IgA, IgG, IgM
- Screen
- CCP
Vasculitis
Phospholipid / Cardiolipin Antibodies (aCL)
Antiphospholipid (aPL) antibodies are a heterogeneous group of autoantibodies to negatively charged phospholipids.
Cardiolipin is the primary antigen associated with aPL antibodies.
The presence of anticardiolipin antibodies (aCL) helps to identify patients at risk for antiphospholipid syndrome (APS).
High aCL levels are associated with thrombosis, fetal loss and thrombocytopenia.
ß2-Glycoprotein I (ß2GPI) facilitates the binding of aCL to the cardiolipin antigen. The detection of aCL and antibodies against ß2GPI is therefore essential for the identification of the APS syndrome.
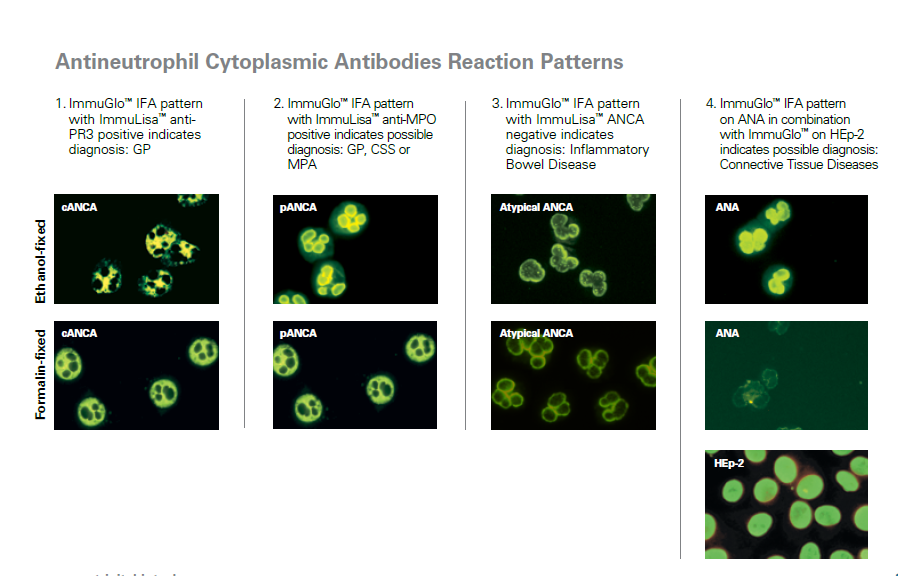
Antineutrophil Cytoplasmic Antibodies (ANCA)
ANCA help in the diagnosis of various necrotizing systemic vasculitis, for example, in granulomatosis with polyangiitis and other small vessel vascular disorders.
In addition, ANCA are also associated with inflammatory bowel disease (IBD), mainly ulcerative colitis, and thus contribute to the distinction of ulcerative colitis from Crohn’s and to the classification of indeterminate colitis.
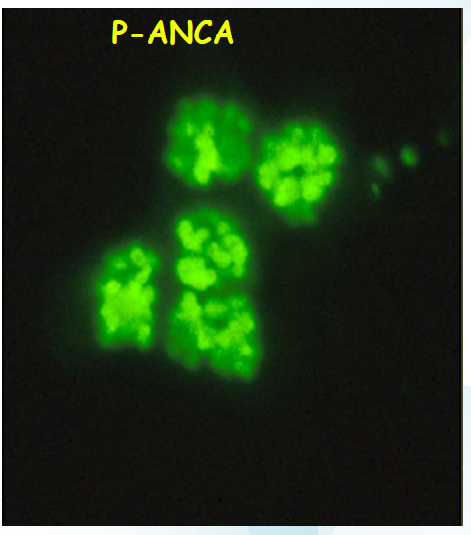
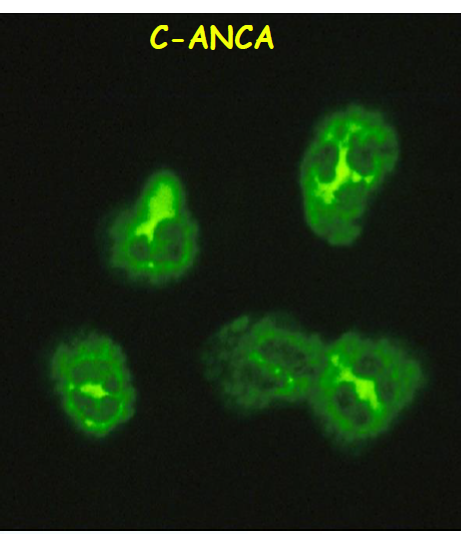
cANCA (cytoplasmic):
- Granulomatosis with polyangiitis
- antigen specificity: PR3
pANCA (perinuclear):
- Polyarteritis nodosa, Churg-Strauss syndrome and ulcerative colitis
- antigen specificity: MPO
Glomerular Basement Membrane Antibodies (GBM-Ak)
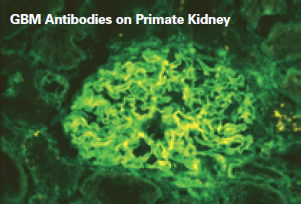
Antibodies to glomerular basement membrane (GBM) occur in glomerulonephritis and in Goodpasture syndrome.
Rapidly progressive glomerulonephritis (RPGN) is characterized by crescentic glomerulonephritis.
Using the above criteria, RPGN can be classified into:
- Immune complex-mediated disease, characterized by the presence of DNA antibodies or streptococcal antibodies
- GBM-mediated glomerulonephritis and Goodpasture syndrome
- Antineutrophil cytoplasmic antibody (ANCA) associated glomerulonephritis
Determination of antibodies in vasculitis
- GBM Antibodies
- Vasculitis LIA (PR3, MPO, GBM)
Antiphospholipid Syndrome (APS)
- aCl Antibodies IgA, IgG, IgM (BILD APS1)
- ß2-Glycoprotein I IgA, IgG, IgM
Antineutrophil Cytoplasmic Antibodies (ANCA)
- ANCA ethanol, formalin fixed
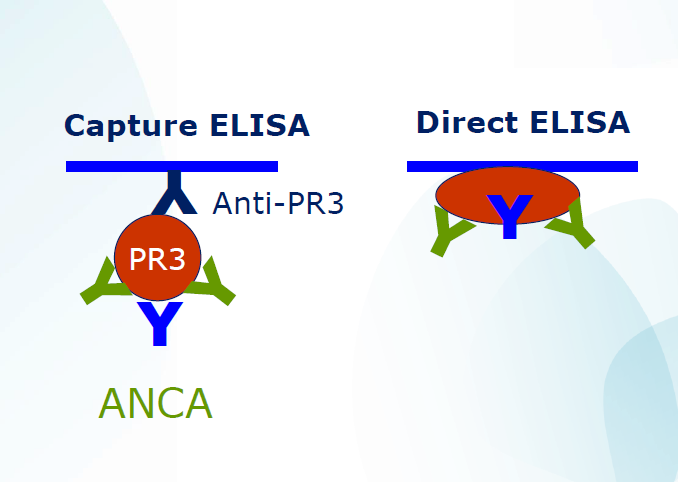
- Capture PR3 ANCA
- Capture MPO ANCA

|
The capture ANCA principle: The wells of the microplate are coated with an anti-MPO / anti-PR3 monoclonal antibody complexed with MPO / PR3. During the first incubation, specific autoantibodies bind to this antigen coating. |

 Deutsch
Deutsch


