LAMP Technology

LAMP = Loop Mediated Isothermal Amplification-Technology:
LAMP technology was developed in Japan in 2000 by Eiken Chemical Corporation (published in Nucleic Acid Research by Notomi T. et al., 2000) and licensed for infection diagnostics by Meridian Bioscience. There exist numerous publications (> 150) about this technology.
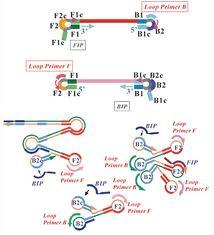
LAMP Process
The technology uses complementary primers to amplify, replicate and expand the DNA fragments to form what is known as a “stem-loop” structure. A total of 6 primers are used for this, which make the reaction fast and specific. In the process, the waste product called magnesium pyro-phosphate is formed, which leads to cloudiness. This turbidity is measured at the end of the reaction and is proportional to the amount of DNA in the sample. The results are evaluated qualitatively.
Since the LAMP technology is ISOTHERMAL, only one temperature, 63°C, is used and the whole reaction happens simultaneously. This means that no conventional "thermal cycler" is required, which on the other hand enables a cost-effective test system.
As the first application based on LAMP technology, Meridian Bioscience has launched a molecular Clostridium difficile test - Alethia® Clostridium difficile Test - on the market.

Background:
Clostridium difficile is one of the most important causes of hospital-associated infections today. C.difficile infections (CDI) also occur in the general population and in farm animals. They are no longer to be regarded as an unpleasant complication after antibiotic therapy. Since 2001, the prevalence and severity of C. difficile infections has increased significantly, leading to increased interest in research and the discovery of new virulent factors. This has expanded the focus in the development of new treatment and prevention methods.
The course oft he disease in humans caused by C. difficile varies from asymptomatic colonization, diarrhea, pseudomembrane colitis, toxic "megacolon" to death.
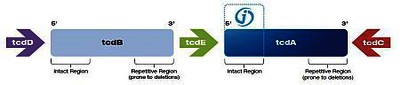
The pathogenicity of Clostridium difficile is associated with the production of two toxins, toxin A (enterotoxin) and toxin B (cytotoxin). The genes for toxin A and B (tcdA and tcdB) are part of the 19.6-kb long genetic pathogenic locus, which also contains 3 other genes, tcdD, tcdE, tcdC, and is the prerequisite for virulence.
Clostridium difficile strains contain this pathogenic locus (PaLoc) and are toxic or, in the absence of PaLoc, non-toxic. Some strains contain atypical or variant toxin A and B genes and can cause the disease. Binary toxin can also be present, but its significance is still disputed.
According to the guidelines of the European Society of Clinical Microbiology and Infectious Diseases (ESMID), American Society for Microbiology (ASM) and Infectious Diseases Society of America (IDSA) together with the Society for Healthcare and Epidemiology of America (SHEA), Clostridium difficile diagnostics recommended as a one- or two-step algorithm.
A molecular test can be used as a singular method.
We can also offer the molecular Alethia® Clostridium difficile Test.
Molecular Analysis:
Molecular analysis of C. difficile started in the 1980s and a reference strain VP-10463- has been identified. Scientists have detected various changes such as deletions, insertions, point mutations in the sequencing patterns. With these variations, Dr. Rupnik and her colleagues developed a toxin typing model that characterizes the various C.dfficile toxin types.
> 30 toxin types are currently known and most of the changes occur in the unstable 3’prime end of the genes, known as the GROP region.
(Rupnik, Maja “Heterogeneity of large clostridial toxins: importance of Clostridium difficile toxinotypes” FEMS Microbiol Rev. 2008 May;32(3):541-55. Epub 2008 Apr 3. Review).
Target sequence of the molecular Alethia® Clostridium difficile test:Meridian has chosen a sequence of 204 bp at the stable 5’prime end of the tcdA gene as its target. This occurs in all C.difficile toxin types and all phenotypes - A- / B +, A + / B +, A + / B- and A- / B- - can thus be detected.
How does the test work?
Meridian has developed a simple and fast molecular test system based on the LAMP = Loop Mediated Isothermal Amplification technology.
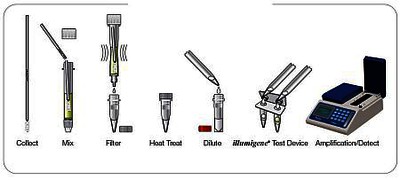
The test kit contains all the necessary reagents in user-friendly test vessels; Sample preparation tube, extraction tube, reagent buffer tube and Alethia® reaction tube.
The test is prepared in a few simple steps and the amplification and detection of the Alethia™ C.difficile target in the PaLoc-Gen is carried out with the illumipro-10™ instrument.
The total test duration is less than 60 minutes.
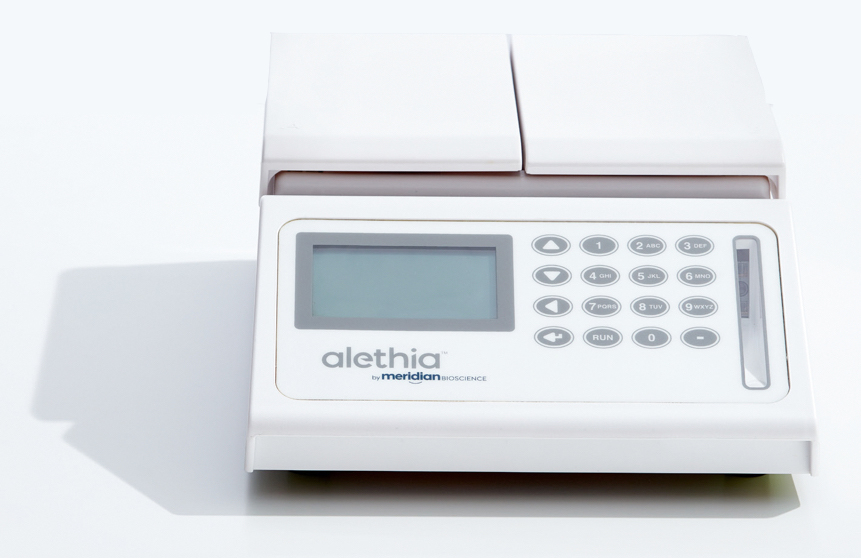

Alethia™ Workstation:
-
A practical aid for the work steps
Components of the kit and test procedure:
Performance data of the Alethia® C.difficile test:
|
Sensitivity |
Specificity |
No Samples |
|
|
Meridian Package Insert Study |
95.2% |
95.3% |
697 |
|
Noren et al, JCM 2011 |
98.0% |
98.0% |
272 |
|
Lalande et al, JCM 2011 |
91.8% |
99.1% |
472 |
|
Doing et al, DMID 2012 |
97.8% |
99.4% |
446 |
|
Boyanton et al, JCM 2011 |
95.2% |
96.6% |
139 |
NPV > 99% PPV > 92%
Available test kits:
Available instruments:
Precise instructions, literature and other information on all products are available from us.
For the complete range of Meridian Bioscience products, please visit our webshop.

 Deutsch
Deutsch


