Parasitology
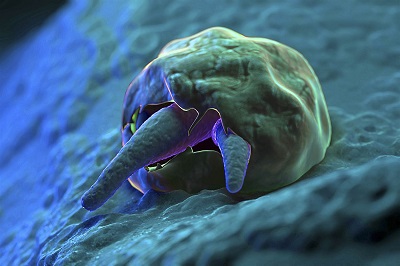 Cryptosporidium parvum
Cryptosporidium parvum
Cryptosporidia are spread worldwide. In humans, infections are caused especially by C. hominis and C. parvum. Asymptomatic infections also occur and carry a high risk of infection. Therefore, a targeted diagnosis for e.g. C. parvum is indicated for diarrhoea of unexplained cause. In addition to the microscopic detection of oocysts, diagnosis of a Cryptosporidium infestation can also be performed immunologically with labeled antibodies or by RT-PCR.
- Microscopic diagnostics
- Rapid tests
- Nucleic Acid Amplification Technique
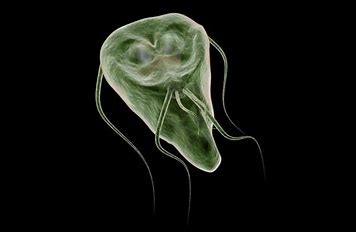 Giardia lamblia
Giardia lamblia
This infectious, human pathogenic endoparasite is spread worldwide and is the causative pathogen of giardiasis. Infection usually occurs as a result of direct smear infection or even oroanal sexual intercourse. Adults acquire the cysts through food, drinking water and ingestion of surface water while bathing in contaminated waters. Giardia Lamblia oocysts can be detected by microscopic examination of wet mount samples, immunologic detection using fluorescent antibodies, or by rt-PCR.
- Microscopic Diagnostics
- Rapid Tests
- ELISA
- Nucleic Acid Amplification Technique
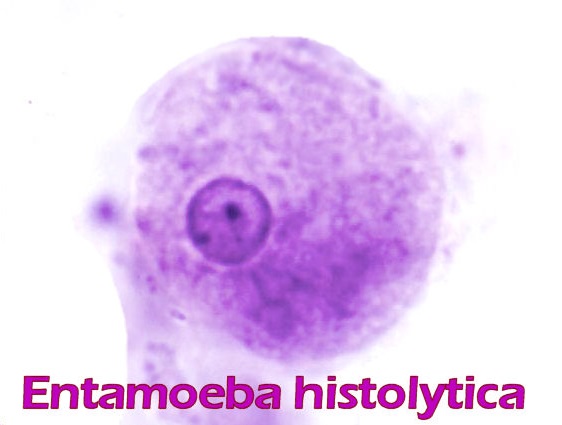 Entamoeba histolytica
Entamoeba histolytica
This human pathogenic intestinal amoeba occurs mainly in tropical and subtropical regions of the world and causes amebiasis, a disease that affects nearly 10% of the world’s population. The classic route of infection is fecal-oral transmission. The incubation period can be from days to years. A common complication is the hematogenous spread of the amoebae into the liver with involvement of the hepatic parenchymal cells and resultant necrotization-infested tissue. We offer a wide range of products for immunological and RT-PCR detection of the pathogen.
- Microscopic Diagnostics
- Quick Test
- ELISA
- Nucleic Acid Amplification Technique
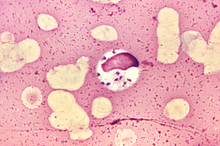
Leishmania Donovani
Leishmania donovani is a species of intracellular parasites belonging to the genus Leishmania, a group of haemoflagellate kinetoplastids that cause the disease leishmaniasis. It is a human blood parasite responsible for visceral leishmaniasis or kala-azar, the most severe form of leishmaniasis. It infects the mononuclear phagocyte system including spleen, liver and bone marrow. Infection is transmitted by species of sandfly belonging to the genus Phlebotomus in Old World and Lutzomyia in New World.
- Mikroskopische Diagnostik
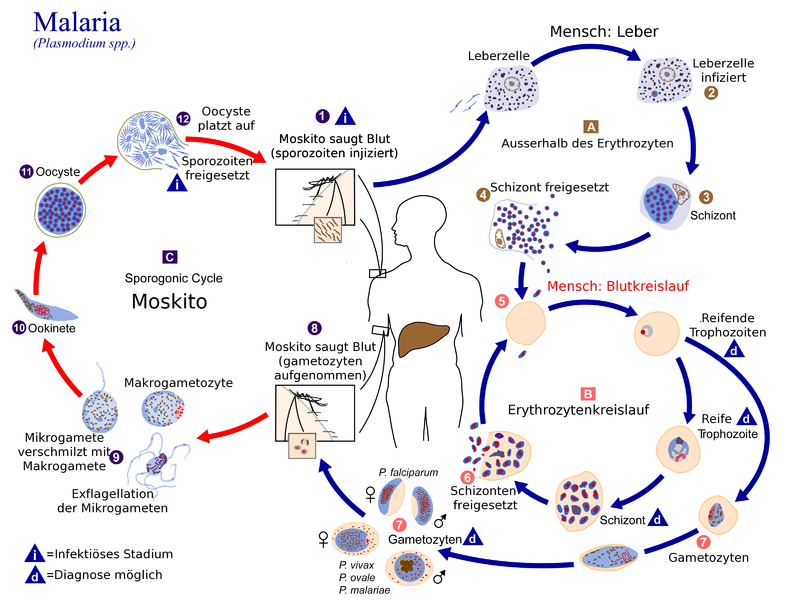
Plasmodium ssp.
Protozoa of the genus Plasmodium cause malaria. There are several human pathogenic Plasmodia species: P. falciparum (causative agent of malaria tropica), P. ovale and P. vivax (causative agent of malaria tertiana), P. malariae (causative agent of malaria quartana) and P. knowlesi. The morphology of these parasites is characteristic for each species and stage of development. Plasmodia are intracellular parasites, and their developmental cycle is twofold: one cycle in the human host and one in the over-carrier mosquito. A direct infection from person to person is not possible.
In our portfolio you will find some molecular tests for reliable malaria diagnostics.
- Nucleic Acid Amplification Technique
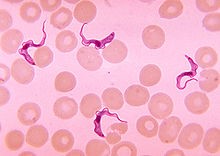
Trypanosoma
Trypanosomes infect a variety of hosts and cause various diseases, including the fatal human diseases sleeping sickness, caused by Trypanosoma brucei, and Chagas disease, caused by Trypanosoma cruzi.
- Mikroskopische Diagnostik

 Deutsch
Deutsch