Gastroenterological Autoimmune Diseases
Inflammatory Bowel Disease: Ulcerative Colitis (UC) and Crohn's Disease
Antineutrophil cytoplasmic antibodies (ANCA)
Anti-Saccharomyces cerevisiae antibodies (ASCA)
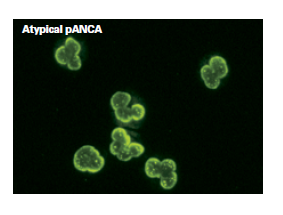
In approximately 80% of patients with ulcerative colitis and approximately 25% of patients with Crohn's disease, atypical pANCA patterns are detected.
These atypical pANCA patterns are characterized by inhomogeneous staining of the perinuclear area.
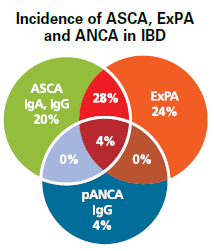
ASCA and ANCA are suitable for screening for inflammatory bowel disease (IBD), for distinguishing ulcerative colitis from Crohn's disease, and for correctly identifying patients with undetermined colitis.
|
|
Prevalence pANCA |
Prevalence ASCA |
|
Ulcerative colitis |
50-80% |
¯ |
|
Crohn's disease |
10-20% |
50-60% |
Exocrine pancreatic antibodies (ExPA)
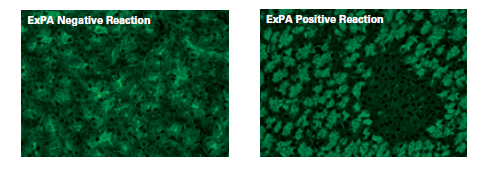
Exocrine pancreatic antibodies are very specific serological markers for Crohn's disease. ExpA are circulating antibodies that react with secretory granules in the cytoplasm of exocrine pancreatic cells.
By IFA - using a primate pancreatic substrate - their presence is demonstrated by a specific reticulo-granular green fluorescence in the cytoplasm of exocrine pancreatic cells.
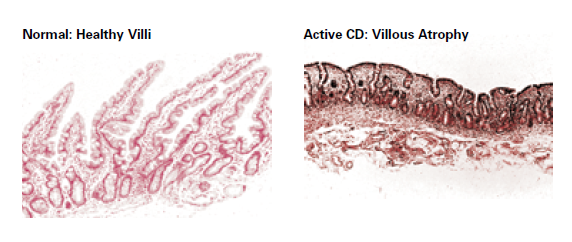
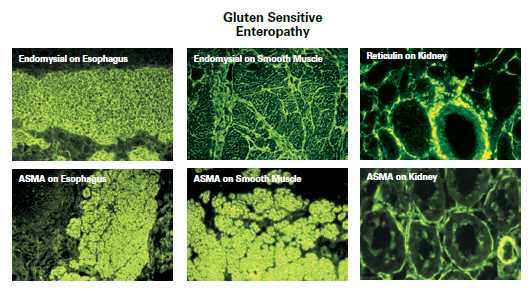
Celiac Disease
Celiac disease is a common clinically heterogeneous gastrointestinal disorder that may have non-classic or minimal symptoms. The patients have antibodies to tissue transglutaminase, endomysium, reticulin and gliadin.
The European and North American societies for pediatric gastroenterology and nutrition recommend the use of serological tests in patients suspected of having celiac disease in order to reduce the number of bowel biopsies required.
These include tests on tissue (tissue) transglutaminase (tTG), gliadin (AGA) and endomysial antibodies (EMA).
Tissue Transglutaminase Antibodies
Tissue Transglutaminase (tTG) was identified as the endomysial antigen that led to the development of ELISA methods for the detection of antibodies in sera from patients with celiac disease.
Several studies have found that the specificity and sensitivity of this method range from 90 to 95 percent.
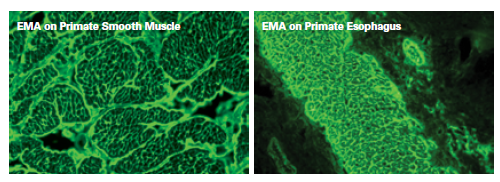
Endomysial antibodies (EMA)
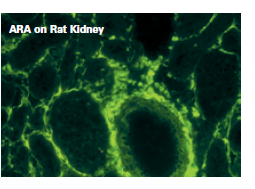
Reticulin antibody (ARA)
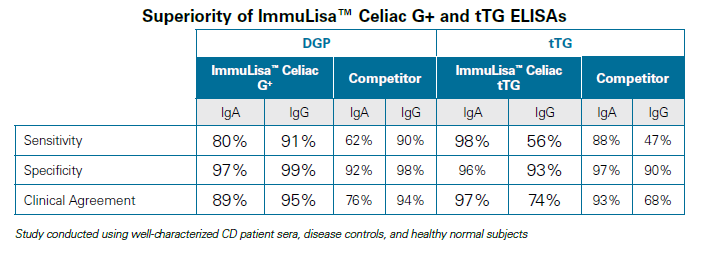
Antibodies to deamidated gliadin peptides (DGP) / anti-gliadin antibodies
Both IgA and IgG gliadin antibodies are detected in sera from celiac disease patients.
Determination of antibodies in gastroenterological autoimmune diseases
Inflammatory bowel disease (IBD): Ulcerative colitis (UC) and Crohn's disease:
- ANCA (ethanol, formalin fixation)
- Exocrine Pancreatic Antibodies (ExPA)
Celiac Disease:
- EMA Antibodies (smooth muscle, distal esophagus)
- Reticulin Antibodies (IgA / IgG)
- Tissue Transglutaminase Antibodies (IgA / IgG)
- Deamidated Gliadin Peptide (DGP) / Anti Gliadin Antibodies (IgA / IgG)
Line Immuno Assay:
- Gastro LIA
- D-gliadin, tTG, ASCA, PCA, Intrinsic Ffactor

 Deutsch
Deutsch


